
Cellular Differentiation · Anatomy and Physiology
herin cell surface levels in a variety of mammalian tissues. Structural studies of the E-cadherin-p120 complex revealed that the cadherin JMD contains two types of p120-binding interfaces. The core p120-binding region is a highly conserved series of residues
Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology
Vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin is a strictly endothelial specific adhesion molecule located at junctions between endothelial cells. In analogy of the role of E-cadherin as major determinant for epithelial cell contact integrity, VE-cadherin is of vital importance for the maintenance and control of endothelial cell contacts.
RNA Molecule Protects Stem Cells During Inflammation Beyond the Dish
herin homophilic cell-cell adhesion molecule are expressed differentially in developing and ma-ture brains, each being expressed in restricted neuronal groups. Cadherin-6 (cad6) is one of such cadherins. Recent studies of cad6 mRNA expres-sion in the postnatal mouse forebrain showed that it occurs in neurons constituting a specific

Cellular Differentiation Anatomy & Physiology I
herin cell adhesion complexes which control the epithelial tissue architectural integrity, while the protein also play a key role in the WNT/β-catenin pathway 13. In addition, epithelial cell.

Atlas ana path_m_herin
in cell culture, where it was demonstrated that disruption. If the interaction of catenins with the cad-herin cytoplasmic tail is disrupted in the intestinal cells of a mouse by tissue-specific transgenic overexpression of a competing cadherin cytoplasmic tail, critical cell-cell ad-hesion necessary both to form and to maintain the epi-

Physical Defenses of the Host Microbiology
cells (for review see Fagotto and Gumbiner, 1996). Although -catenin is a critical component of the cad- Address correspondence to Barry M. Gumbiner, 1275 York Ave., Box herin cell adhesion complex, it also has a well-established 564, New York, NY 10021.
Blood cell development illustration
Stem cell shape regulates a chondrogenic versus myogenic fate through Rac1 and N-cadherin. 2010 Mar 31;28 (3):564-72. doi: 10.1002/stem.308. Department of Bioengineering, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, USA. Human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs) are multipotent cells that can differentiate into many cell types.

THE NUCLEAR MEMBRANE BIOLOGY 1 H YouTube
herin in noninvasive, E-cadherin-positive cells produces an invasive cell, even though these cells continue to express high levels of E-cadherin; the data suggest that N-cadherin-mediated cell motility may be stimulated by FGF receptor signaling; and other cadherins, such as cadherin-11, may promote motility in epithelial cells in a manner.
Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology
DOI: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2021.01.014 Corpus ID: 231760370; Intraepithelial Lymphocytes Suppress Intestinal Tumor Growth by Cell-to-Cell Contact via CD103/E-Cadherin Signal @article{Morikawa2021IntraepithelialLS, title={Intraepithelial Lymphocytes Suppress Intestinal Tumor Growth by Cell-to-Cell Contact via CD103/E-Cadherin Signal}, author={Ryo Morikawa and Yasuhiro Nemoto and Yukinori Yonemoto and.
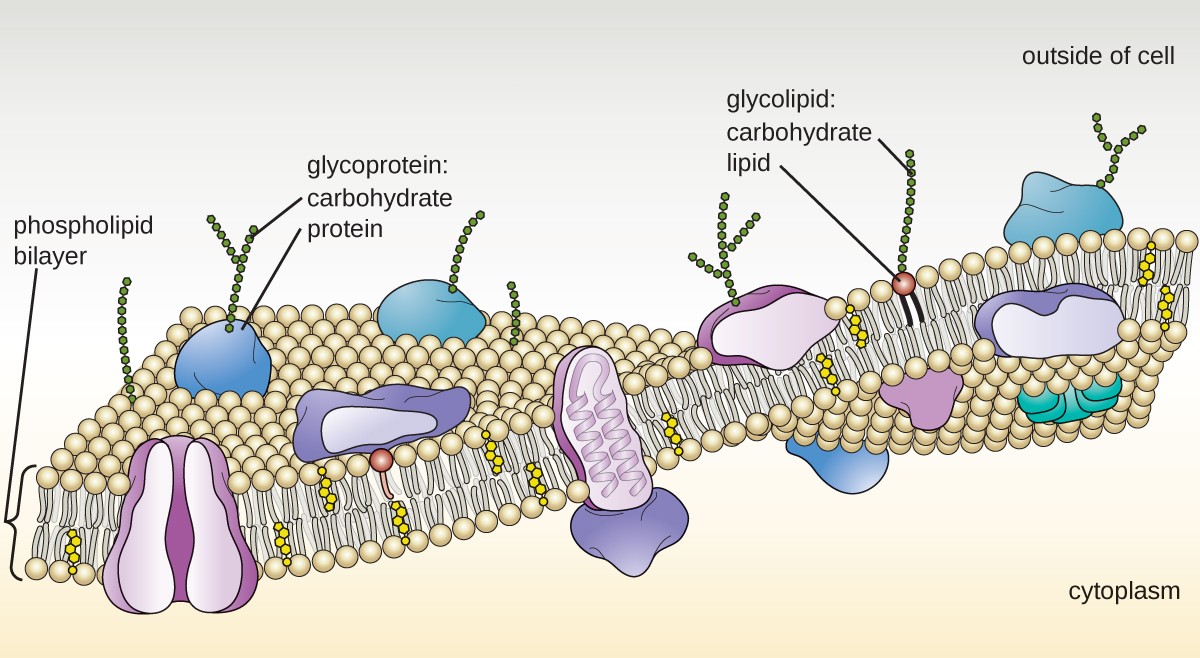
Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology
Cadherins may also contribute to cell segregation by dif-ferential levels of expression of a single cadherin type (Stein-berg, 1970). Indeed, cells expressing high levels of cadherin will sort out from cells expressing low levels of the same cad-herin (Friedlander et al., 1989; Steinberg and Takeichi, 1994).

e correlatio ion between n immuno ostaining o of Ecadh herin and
Furthermore, an evolutionarily conserved cdc2 phosphorylation site (Thr-927) in HsEg5 is phosphorylated specifically during mitosis in HeLa cells and by p34cdc2/cyclin B in vitro. Mutation of Thr-927 to nonphosphorylatable residues prevents HsEg5 from binding to centrosomes, indicating that phosphorylation controls the association of this motor.

Unique Characteristics of Eukaryotic Cells Microbiology
either high-E-cadherin cells, low-E-cad-herin cells, or both through the use of an Itgb1-sgRNA. Bud formation was abol-ished both in high/low-E-cadherin cells and in low-E-cadherin cells alone. Impor-tantly, loss of b1-integrin in only high-E-cadherin cells did not significantly affect budding.Theseresultsindicatethatb1-in-
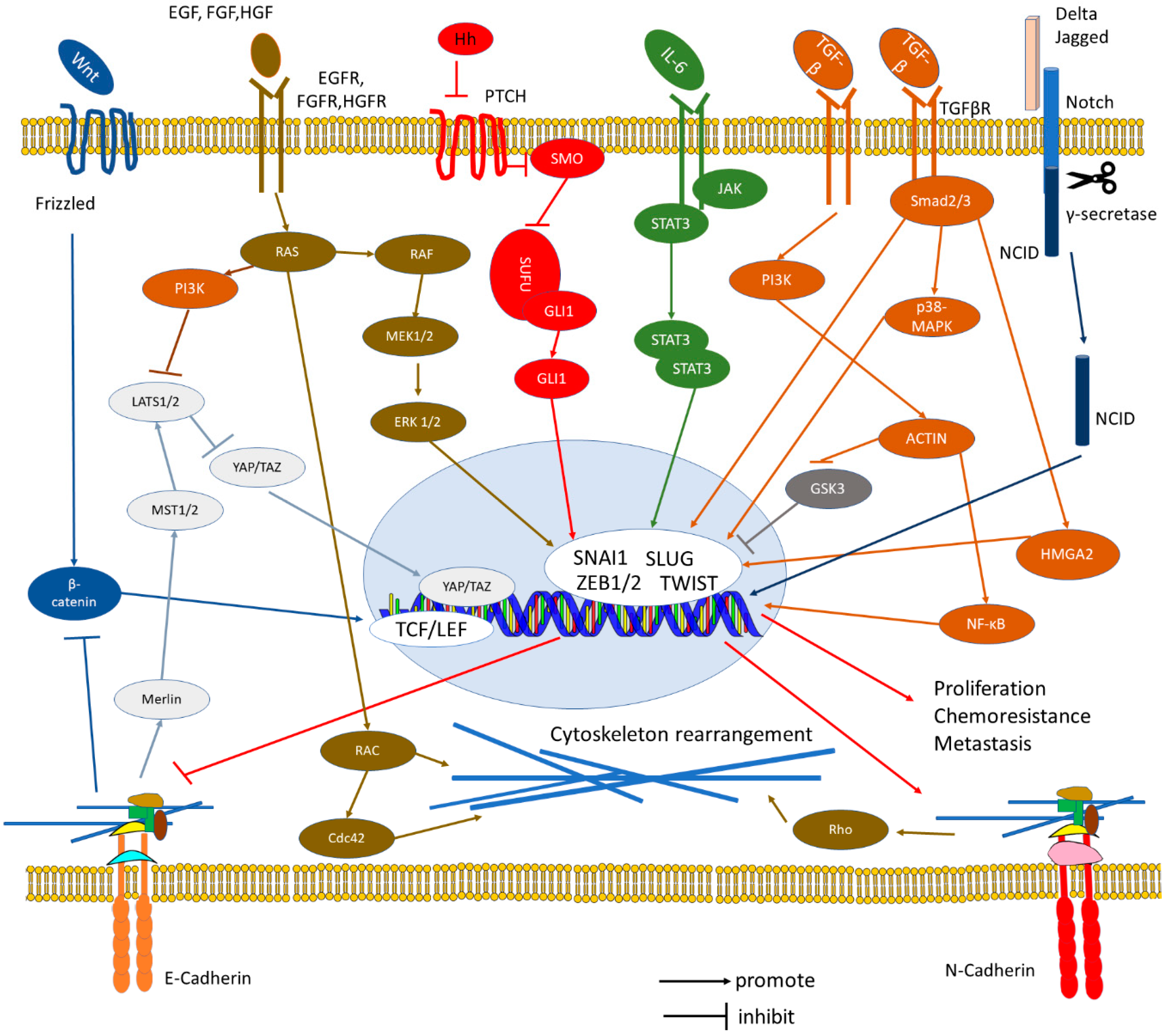
Cells Free FullText The ECadherin and NCadherin Switch in
Pathophysiology. Epithelial cadherin (E-cadherin) is a transmembrane protein ( Histopathology 2016;68:57 ) Extracellular domain involved in intercellular adhesion and polarity maintenance. Cytoplasmic domain attached to actin units α / γ / β- and p120 catenins. Encoded by CDH1 (CaDHerin-1) gene located on chromosome 16 (16q22.1)
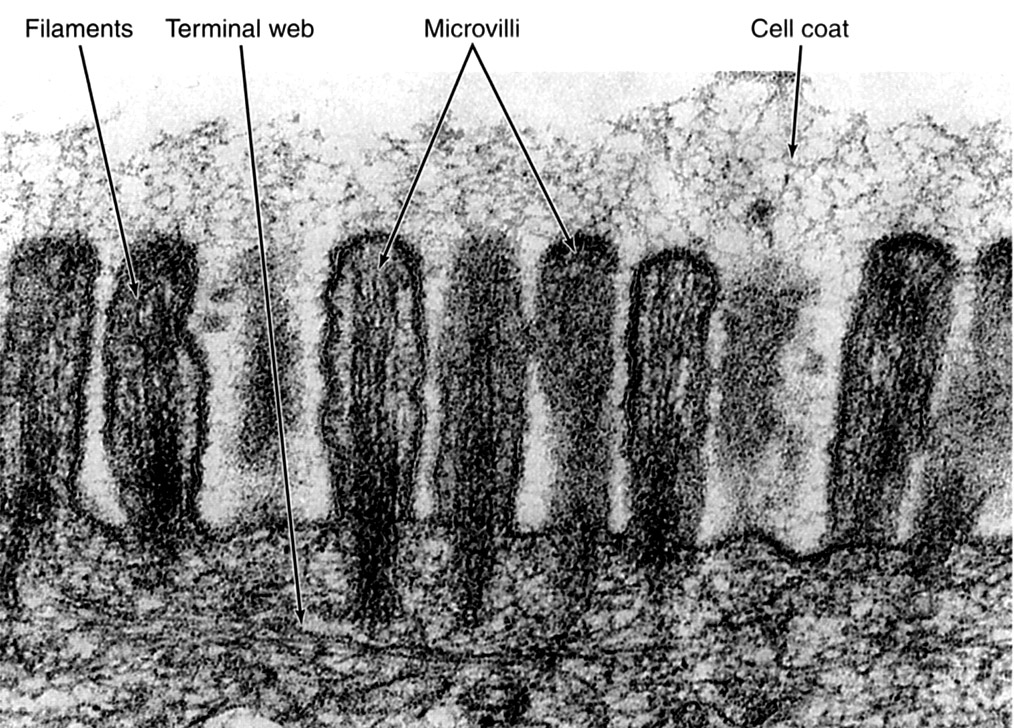
Electron Micrograph
herin; also known as cadherin 1), antibodies that block the adhesive function of VE-cadherin dissociate endothelial cell layers in vitro [24] and enhance neutrophil extravasa-tion [25] and vascular permeability [26] in vivo. Despite there being several other adhesion molecules located at endothelial cell contacts, the antibodies directed against

Cells
Cadherins constitute a class of morphoregulatory proteins that bind to identical proteins on cell surfaces to mediate cell-cell adhesion in all soft tissue (1-3).They also facilitate cell sorting during tissue morphogenesis (1-4).These are single-pass transmembrane glycoproteins, and the homophilic association of identical opposed cadherin extracellular (EC) segments maintains the.

HERIN CELL
herin cell adhesion system by various mechanisms during mul-tistage human carcinogenesis. The structure of β-catenin is remarkably similar to that of the Armadillo protein, an important element in the Wingless/Wnt signaling pathway of the fruit fly Drosophila.6, 7) Wingless is a cell-cell signal in Drosophila that triggers many key develop-